
What is data lineage?
Data lineage is the process of tracking data through its lifecycle, from creation to end destination. It provides a record of where data originates, how it moves through your organisation and how it gets transformed along the way.
Think of it as a roadmap, showing the route your data has taken through your organisation and all the stops it has made along the way.
Why is data lineage important?
By being able to trace the lineage of a piece of data, organisations can improve the quality of their data, enhance compliance and make better business decisions.
Data quality: with clear data lineage, firms can more easily spot inconsistencies and errors within their data. This empowers them to take corrective action and prevent further issues moving forward. It can also aid in disaster recovery and backup should anything go particularly awry.
Better decision-making: by maintaining the accuracy and consistency of their data across its lifetime, organisations can ensure the quality of their data. This has numerous benefits, including the ability to make better data-driven business decisions and reduce the risk of costly errors.
Improved security: data lineage is essential in keeping your data secure as it helps to identify any potential breaches or vulnerabilities across your organisation’s data pipeline. This, in turn, helps maintain trust in your data and safeguards your company’s reputation.
Compliance and transparency: transparency is another key benefit of tracking data lineage. By providing a complete view of a piece of data across its lifetime, organisations can ensure they are complying with both internal data governance policies and external regulation.
Is it essential for every organisation?
Data lineage is essential for any organisation that uses data. The clarity it provides helps every business – big and small – make informed decisions, maintain accuracy and manage their data effectively.
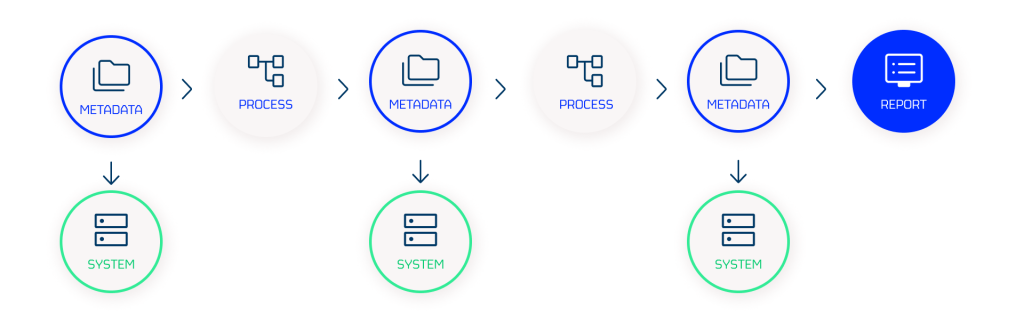
Data lineage in action
Data lineage plays an important role in compliance and governance. This is because it allows organisations to understand the origins of a piece of data and the transformations it may go through as it passes through their systems. Through this, organisations can ensure and track whether their data is being used appropriately and in accordance with any external regulation or internal policies.
This, in turn, supports organisations in maintaining the security of their data. This is because teams have greater visibility into how any sensitive data moves within their company, including where it is stored and who has copies of it. As a result, they can make sure the appropriate controls are put in place regarding access and permissions. It is also a valuable tool in identifying the source of security incidents. This is because teams are able to see the full journey of a piece of compromised data, allowing them to more easily pinpoint the source of a breach. This helps in improve response times, contain incidents and minimise any damage that could potentially occur.
Similarly, tracking data lineage is useful for root-cause analysis. By providing a map that shows how data has been modified over the course of its lifecycle, organisations can quickly isolate when and where errors or discrepancies arose. This enables teams to take corrective action.
Tracking data lineage also empowers teams to prevent similar issues in the future by enabling impact analysis. This is because when you have a complete overview of your data ecosystem, you can better understand the dependencies within it and anticipate any disruptions or inaccuracies that might occur if you were to make a change. Through this, organisations can benefit smoother migrations as they can better identify issues, bottlenecks or upgrade requirements in advance.
How does it work?
Data lineage requires an organisation to capture, track and document the movement of data across and through its system. At a high-level, this typically involves:
Discovery: identifying all data sources within an organisation and establishing relationships between entities.
Tagging: assigning metadata tags to build a rich and comprehensive picture of a data asset.
Tracking: continually recording the journey of a data asset from source to destination, noting the processes it goes through and any transformations that occur along the way.
Documentation: capturing data lineage information in a standardised and comprehensive way, enabling users to understand and analyse the movement of data across an organisation.
What are the challenges?
Data ecosystems within organisations can be complex. They can evolve rapidly as teams introduce new pipelines and make updates or changes. This dynamic backdrop presents challenges for tracking data lineage, especially if an organisation is attempting to do it manually.
The sheer volume of data today, and its rapid generation and diverse formats, can mean firms require sophisticated tools and methodologies to effectively keep track of data as it moves through their organisation. These solutions then need to keep pace with changing regulations and evolving business requirements. This can end up a time-consuming and resource-intensive process for businesses.
Research conducted by A-Team Insights found the top three challenges delaying data lineage projects were concerns around technological complexity, a poor understanding of data lineage within their business, and a lack of management buy-in or a lack of budget and resources.

Five best practices for implementing data lineage
As we’ve discussed, the increasing complexity of businesses’ data ecosystems in the last couple of decades has made tracking data lineage more and more difficult. But, by adhering to a few simple principles, your firm can drive a successful implementation:
- Standardise naming conventions: enforce consistent naming conventions to reduce confusion and simplify tracking.
- Document data sources: maintain detailed documentation of all data sources within your organisation.
- Define clear ownership: establish ownership and stewardship of data assets to ensure accountability for its quality.
- Continually audit and update: schedule periodic audits to identify any gaps or inconsistencies.
- Automate: automate your data lineage capture so you can avoid the risk of human error and speed up your processes.



