
Financial messaging standards are essential in supporting the smooth exchange of information and data between financial institutions. They provide a common language that makes communication efficient, unambiguous and machine friendly.
However, the increased demand for faster payments, 24-hour service and around the world connectivity has tested the limits of these standards in recent years and exposed the failings that result when financial institutions aren’t always speaking in the same language.
The industry hope that by mandating an innovative new global standard, known as ISO 20022, these issues can be resolved.
What is ISO 20022?
Developed by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO), ISO 20022 aims to create a common language and model for payments, securities, foreign exchange and trade services.
It supports richer and more structured data in messages and is far more flexible than its predecessors. This is because ISO 20022 leverages the descriptive, comprehensible and hierarchical XML format.
This format means messages can contain around ten times more data compared to legacy standards. Also, because the XML format allows users to define custom tags to structure data, it is more flexible and more easily shared across different systems. This plays a crucial role in improving interoperability and maintaining consistency.
How does it differ to other standards?
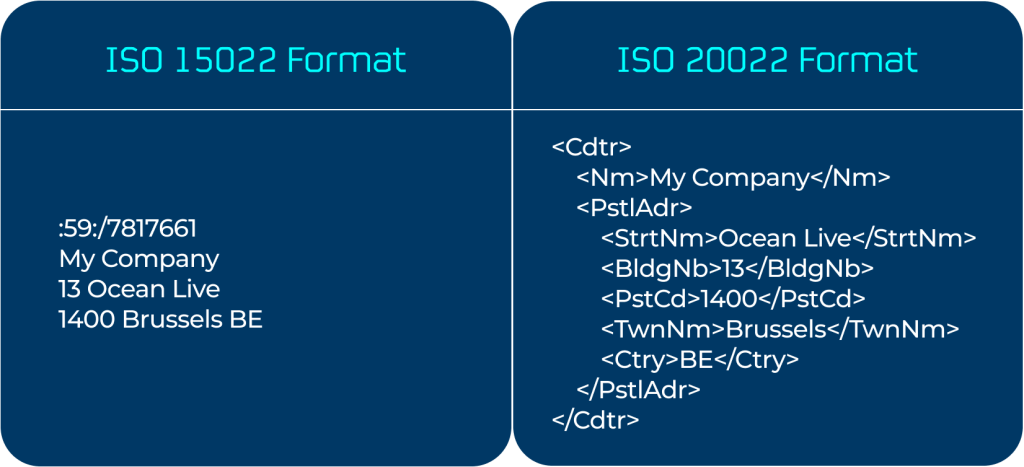
ISO 15022 was the predecessor to ISO 20022.
Introduced in 1998 and mandated in 2003, the standard improved Straight Through Processing (STP) rates substantially. In the securities clearing and settlement industry, for example, the transition to ISO 15022 increased STP rates from around 60% to more than 95%.
However, ISO 15022 messages support a limited set of fields and have an extremely constrained number of characters. This limited size and structure increases the risk of losing critical information when messages are exchanged between financial institutions and slows down transaction processes.
What are the benefits of ISO 20022?
Improved interoperability: by creating a common language across international payment systems, ISO 20022 will make data sharing between financial institutions easier. This will help create a more harmonised financial services industry where collaboration can flourish.
Enhanced transparency: by providing a richer and more structured framework for financial messages, financial institutions can provide far more detailed and complex information. This helps enhance transparency and improves accuracy.
Better insights: with more detailed information contained in each message, financial institutions will be empowered to conduct more in-depth analysis on their data and pull more meaningful insights. This will help businesses make better data-driven decision and potentially open new revenue streams.
Reduce risk: the higher level of detail enabled by ISO 20022 and the identical standards, formats and protocols it will facilitate across financial payments worldwide will help improve fraud detection and keep payments secure.
Future-focused: previous messaging standards were not flexible enough to support a financial industry that was constantly evolving and expanding. ISO 20022 has been designed with flexibility in mind, making it easier for financial institutions to adapt as the business, technology or regulatory landscape changes.
A challenging transition
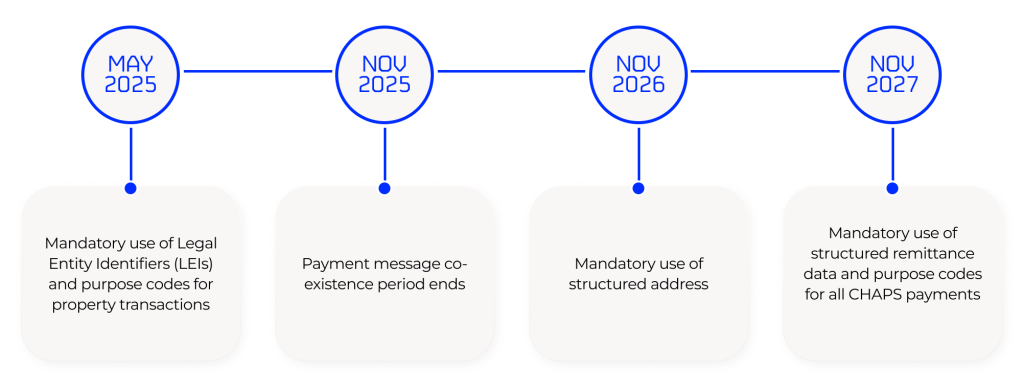
Currently, three quarters of all the payments going through the Swift network are still using legacy formats. As a result, only 40% of the Swift network are expected to be ISO 20022-compliant by November 2025.
Many major banks – such as Barclays, HSBC, and Lloyds – are already live with ISO 20022. However, smaller firms appear to be trailing behind. Often this is down to budget and resource constraints, as well as a lack of know-how, which can hold smaller organisations back from making the transition.
Challenges remain for adopters of a larger size too. The new financial standard is not as forgiving as previous ones. Every character within a message has to be 100% aligned with specifications, otherwise it could be rejected or delayed. This can make the migration from legacy standards a difficult one which requires a solid strategy and comprehensive training.
Failure to meet the challenge could mean businesses lose their competitive edge as other firms can be empowered by ISO 20022 to provide better services to their end-users and leverage more sophisticated insights from their data.
Top tips to get ready for ISO 20022
- Develop a clear roadmap: having a timeline for implementation is vital, as is understanding the functions and departments within your organisation that will be impacted by the transition to ISO 20022.
- Engage with technology partners: adopting ISO 20022 may require investment in new technology, whether that’s upgrading your organisation’s core systems and platforms or your data management tools to support the new standard. Securing quality technology partners that can provide valuable support and insight throughout the migration process will make this easier.
- Educate staff and customers: a comprehensive training programme and a commitment to ongoing support for your team will help ensure the long-term success of your implementation.
How could Raw Knowledge support my firm’s transition to ISO 20022?
At Raw Knowledge, we are currently deploying an innovative new platform that changes the way data is extracted, processed, and verified.
Our Managed Smart Data Platform creates a unified view of disparate data sources, using the power of large language models and cutting-edge platform architecture, to help businesses streamline their operations, make better data-driven decisions, and uncover new revenue streams. Built on a metadata-driven, extensible architecture, our pioneering data management platform is flexible to support several different financial standards, including ISO 20022.
If you’re looking for a data management platform that can support your transition to ISO 20022, or a similar financial standard, we can help.
We want to work with you to understand your pain points around data and data processing so we can adapt our platform to meet your unique needs and drive your business forward.



